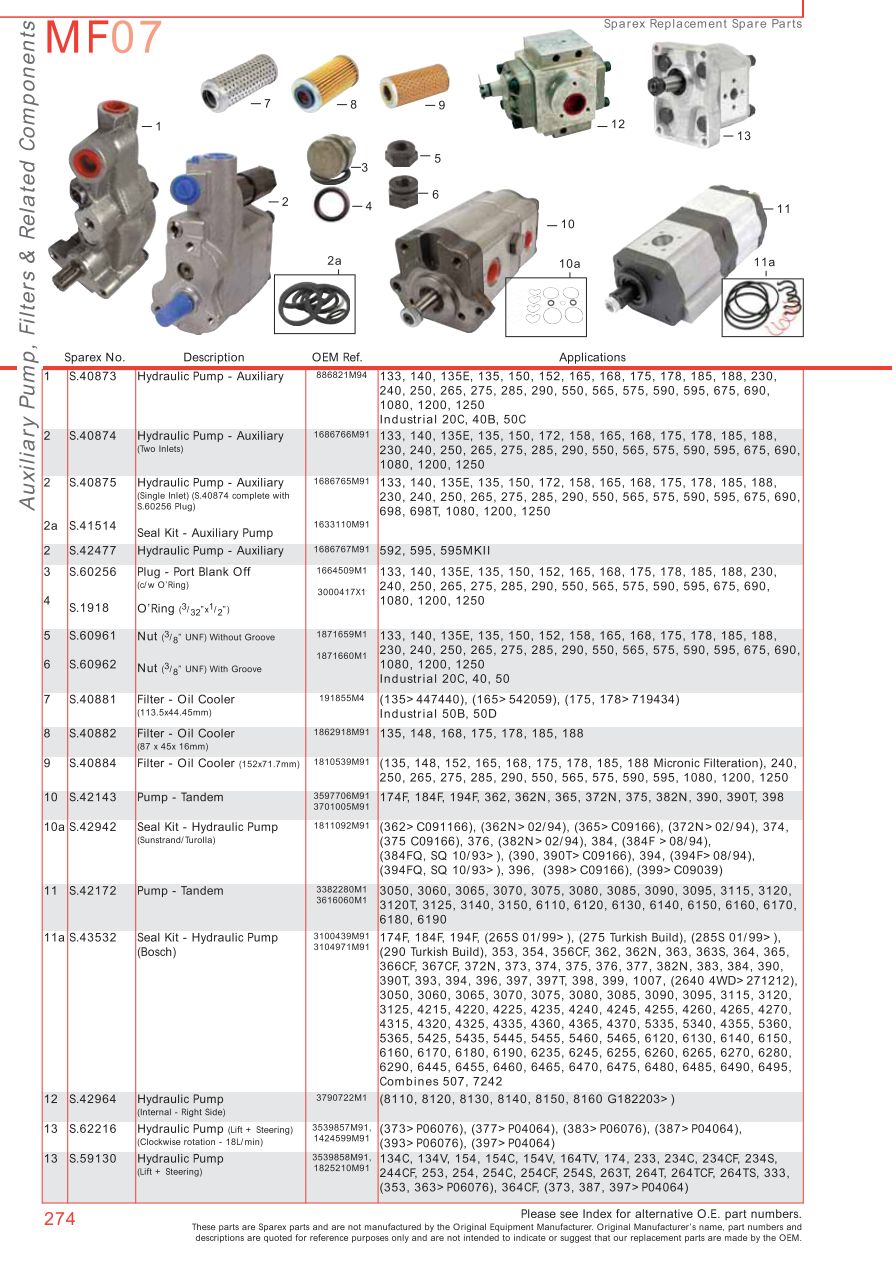
Massey Ferguson Workshop Manual 393
Contents. History The company was founded in 1847 in, by, as the Newcastle Foundry and Machine Manufactory. To begin with it made some of the world's first at first by assembling parts from the, but eventually designing and building its own equipment. Daniel's eldest son, renamed the enterprise the Massey Manufacturing Co. And in 1879 moved it to, where it soon became one of the city's leading employers.
Your Massey Ferguson service manual will come to you in pdf format and is. MF 393 Tractor Service Manual Massey Ferguson MF 390T Tractor Service.
The massive collection of factories, consisting of a 4.4 hectares (11 acres) site with plant and head office at (now part of ), became one of the best known features of the city. Massey expanded further and began to sell its products internationally. Through extensive advertising campaigns it became one of the most well known brands in Canada. A labour shortage throughout the country also helped to make the firm's mechanized equipment very attractive. Massey-Harris Limited.
Share of the Massey-Harris Ltd, issued 18. Manual dodge gran caravan 2017. February 1916 In 1891, Massey Manufacturing merged with to become Massey-Harris Limited and became the largest agricultural equipment maker in the. Massey-Harris made threshing machines and reapers as well as safety bicycles, introducing a shaft-driven model in 1898. In 1910 it acquired the in Batavia, New York, making it one of Canada's first firms. Massey-Harris's early tractor models included the 20 horsepower Massey-Harris GP 15/22 (1930–36), 25 horsepower 'Massey-Harris Pacemaker (1936–39), 35 horsepower (1938–42),. Grain harvesting was revolutionized by Massey engineer in 1938 with the world's first self-propelled combine – the No.
—but it was too heavy and expensive for extensive mass production. However, it served as a guide for the building of the lighter and less costly No. 21, which was tested in 1940 and put on sale in 1941. The Massey-Harris No. 21 Combine was commemorated with a Canada Post stamp on June 8, 1996., one of 's, joined the board of directors in 1942, and joined management in 1946.
The final generation of Massey-Harris tractors, introduced immediately after World War II, included the 25 horsepower M-H 22 series, the 35 horsepower M-H 33 series, the 45 horsepower M-H 44 series and the 55 horsepower M-H 55 series. In 1952 the M-H 22 was replaced by the M-H 23 Mustang. In 1955 the 30 horsepower Massey-Harris 50 was introduced after the merger that created Massey-Harris-Ferguson. It was based on the Ferguson TO-35 and was also produced as the F-40 for Ferguson dealers.
The MH-50 was available in several configurations: utility, high-crop utility, or row-crop with a choice of single, tricycle, or wide adjustable front ends. In 1956 the M-H 33 was replaced by the MH 333, the M-H 44 was replaced by the M-H 444 and the M-H 55 was replaced by the M-H 555. These tractors, commonly known as the 'triple series', were mechanically similar to their predecessors but featured new styling which included a slightly different hood design, chrome trim on the grill and hood, and a different color scheme.
They were also available with power steering, live PTO and hydraulics. The Massey Harris triple series tractors remained in production until 1958. Sawyer-Massey In a complex turn of events, the Massey family turned to steam engine builder L.D. Sawyer & Company of Hamilton, Ontario, and started a line of steam tractors. These engines were quite successful and were built in a number of sizes. The 25 horsepower was popular, and the expanding Prairie provinces clamoured for big breaking engines.
Massey also experimented with tandem. Sawyer Massey lasted only until 1910 when the firm was wound down, and Massey went into.
Sawyer-Massey and Massey-Harris were two separate companies, both managed by the Massey family. Wallis Gas Tractor and wider influence. Main article: In 1955, Massey purchased the Australian manufacturers of Sunshine harvesters,. Had invented the in 1884, the first machine to combine the functions of reaping, threshing and winnowing grain from a standing crop.
By the 1920s, H.V. McKay Pty Ltd was running the largest implement factory in the southern hemisphere, covering 30.4 hectares (75 acres), and led the international agricultural industry through the development of the world's first self-propelled harvester in 1924. In 1930 the H.V.
McKay Pty Limited was granted exclusive Australian distribution of Massey-Harris machinery. The company was then renamed H.V. McKay Massey Harris Pty Ltd. Throughout World War II, H.V. McKay Massey Harris exported over 20,000 Sunshine drills, disc harrows and binders to England to facilitate the increase in food production. In 1955 the remainder of H.V.
McKay Pty Ltd was sold to Massey Ferguson. Manufacturing ended in 1986 and the last section sold off and demolished in 1992. The former bulk store, factory gates and clock tower, the pedestrian footbridge, factory gardens, and head office complex still exist and are all listed on the. Landini In 1959, Massey bought 100% of, based in. Landini has built many models for Massey over the years, especially vineyard and crawler models. Massey sold 66% to in 1989, some to later on, and the final portion was sold to ARGO in 2000.

Perkins In 1959 of, England, was purchased, Perkins having been the main diesel engine supplier for Massey Ferguson for many years. In 1990, Massey Ferguson took over of Stafford and merged it with Perkins to form Perkins Engines (Stafford) Ltd. In the 1980s, Perkins purchased Rolls Royce (Diesels) Ltd, to form Perkins Engines (Shrewsbury) Ltd. Perkins was sold off in 1998 by then owner to, who were a major customer for their smaller and mid-sized engines; Caterpillar was a major producer of large diesel engines for static and mobile application. Ebro of Spain In 1966, Massey purchased 32% of the Spanish tractor and auto company, or Motor Iberica. Ebro had previously built tractors under license, but now began building models for Massey, and Massey models under license. Massey sold its interest to Nissan in the 1980s.
In the early 1960s MF moved their head office from 915 King Street to the Sun Life Tower at 200 University Avenue in the downtown Toronto core. In 1969, Massey Ferguson began producing a line of by the name ' Ski Whiz'. The snowmobile line was discontinued in 1977, due to a decline in sales. Activities in Germany In 1973 Massey purchased German and many Massey-licensed Eichers were built. They later sold their interest, and Dromson now owns Eicher which now builds specialized tractors for vineyards and such. The firm then purchased control of in 1974.
After a loss of $250 million over the next five years, Hanomag was sold off. Conrad Black take-over On 16 August 1978, whose family had obtained control of an investor of Massey Ferguson's, became active in Massey Ferguson's management. The previous year, chairman received a $471,000 salary, the highest executive salary in Canada at the time. During the 50 years between 1929 and 1979, the firm made more than 4% on its sales only five times. Under Black's leadership, Massey Ferguson instituted significant cost-cutting programmes that returned it to profitability. During the late 1970s, production was relocated to a new large facility in.
In 1978 Massey Ferguson was the first to introduce an electronic control system for the three-point hitch on a tractor. However, a worldwide decline in the agricultural equipment market combined with high inflation, high domestic interest rates and a major recession, caused Massey Ferguson to slip into a loss once again. On 31 October 1979, made an informal offer for 51% of the firm, but was rebuffed by Black. On 23 May 1980, Black resigned as chairman. In a subsequent series of detailed and lengthy letters to, then the Canadian under the government of, he remarked on the challenges faced by the firm, and outlined his solution, which would have seen the Canadian and Ontario governments as well as Argus Corporation refloat the ailing firm.
Black failed to obtain a suitable response, and resolved to cut his losses. Renamed to Varity. See also: In October 1980, Argus donated its shares in Massey Ferguson to the employee's pension plans, leading the way to a $250 million bail-out from the Government of Canada and the Province of Ontario for the collapsing business, which later renamed itself Corporation. In the mid-1980s, Varity spun off several money-losing divisions into an entity called Massey Combines Corporation in 1985.
Massey Combines Corporation was headquartered in and became insolvent on 4 March 1988, and its assets were re-acquired by Massey Ferguson. Fermec sale In 1992 a management buyout of MF Industrial created Fermec which finally ceased trading in 2001 when it was taken over by the Corporation (Terex was formerly a unit of ). This encompassed all construction equipment from Massey. It was then purchased by in 1997. Varity left Toronto and relocated to their head offices to the Williams-Butler House at 672 Delaware Avenue in the Millionaire Row area of. The Toronto manufacturing complex has since been demolished, leaving only its head office building. Despite its hardships, Massey Ferguson was selling 25% more tractors than its nearest competitors at this time.
In 1995 Massey Ferguson's worldwide holdings were purchased by the US-based. In August 1996, merged with to become. After a series of mergers and take-overs, the remains of were taken over by the US. Since 1962, Massey Ferguson has been the world's leading tractor brand. Currently, there are more Massey Ferguson tractors than any other, worldwide.

A Massey Ferguson 35 Massey Ferguson developed a wide range of agricultural vehicles and have a large share in the market across the world especially in. In December 1957 the MF35, the first Massey Ferguson branded tractor rolled off the factory floor. It was a Ferguson design that started its life in 1955 as the Ferguson 35, often nicknamed 'Gold Belly' due to the gold engine and gearbox. The 35s were massively popular and sold across the, and the. These were followed by other early models like the (MK1 indirect injection) 65 (MK2 direct injection).
The next big selling model was the MF135, widely popular because of its reliability and power compared with other tractors at the time. This was the first model in the MF 100 series. These included the MF 135, 145, 148, 150, 165, 168, 175, 178, 180, 185 and 188.The same time the MF 100 series came out, the MF 1000 series was introduced. These include the MF 1080, 1100, 1130 and 1150. Later came the MF 550, 560, 565, 575, 590, 595 (500 series). From the mid-1970s and early 1980s came the 200 series tractor, which included the MF 230, 235, 240, 245, 250, 255, 260, 265, 270, 275, 278, 280, 285, 290, 298, 299. In the mid-1980s, the short-lived 600 series was released.
This included the 675, 690, 690T, 695, 698 and 699. The reason for poor sales figures was due to unattractive styling and poor ergonomics, with the cab sitting much higher than previous MF tractors. Although the cab did give excellent visibility and a flat floor, being high off the ground meant it was best suited to field operations instead of livestock work.
The 600 series was one of the first tractors to offer the user an option to control where the hydraulic fluid should be pumped. By moving a switch situated near the floor of the cab, the user could block off flow to the rear hydraulics and link arms, concentrating the full force of the pump on the front loader if equipped. In the late 1980s, one of the greatest selling tractors of all time was released- the 300 series Massey Ferguson.
Excellent power, simplicity of cab, high range of and components made the MF 300 series a success especially in. The range included the MF 350, 352, 355, 362, 365, 372, 375, 382, 383, 390, 390T, 393, 394, 395, 398, 399 and 399T (the most powerful and popular ) with horsepower ranging from 52HP to 104HP. The 300 series was also offered with a choice of cab, Hi-Line or Lo-Line. The Hi-Line cab featured a flat floor whilst the Lo-Line cab had a hump in the middle for the transmission tunnel. Some 'original' examples of the lower horsepower 300-series have been known to fetch prices exceeding £20,000 because of their rarity.
In the mid-1990s, the 6100 series and 8100 series were released, including the 6150, 6180 and 8130. Massey Ferguson MF 8290 tractor towing a grain trailer Tractors that came after the 300 series included the 4200 range, the 4300 range, 3600 (early 1990s), 3000/3100 (early to mid-1990s), 3005/3105 (mid-1990s), 6100 (late 1990s), 6200 (late 1990s/early 2000s (decade)), 8200 (late 1990s/early 2000s), 5400, 6400, 7400, 8400, 7600, (2012 to 2014) and 8600 (2009 to current). Today Massey Ferguson currently produces 8600 series (limited markets),5400 (limited markets), 5600, 6600, 7700, 8700 series tractors. (AGCO Beauvais France) Massey Ferguson tractor production factories also build tractors marketed by AGCO under the ' brand, and also specific model ranges for. In June 2012, the Agco facility in, was expanded to start building Massey Ferguson and comparable AGCO 'Challenger' models for the North American market. Since production commenced at AGCO Jackson, the facility has produced '7600' series and '8600' series Massey Ferguson tractors for the North American market.
Currently in production at the Jackson facility are the recently released 7700 and 8700 series Massey Ferguson tractors. Product images. Massey Ferguson 8732 Licensees Massey Ferguson is the most widely sold brand of agricultural machinery in the world. The brand and designs are or were licensed to a variety of companies around the world including:. AEIG – Aftab Ekbatan Industrial Group, current exclusive licensee of Massey Ferguson Tractors in.
Ebro – Spanish company purchased and later sold by MF. Eicher – German company purchased and later sold by MF. Farmwell – assembled by Samarakoon Tractor Industries Private Limited in. GIAD – assembled by the in. – Industrija Mašina i Traktora in. ITMCo – Iran Tractor Mfg Co in.
Own/sell under VenIran, TajIran, MFT and Eder Derdison names. – Italian company purchased and later sold by MF. licensee in. Sutcliff – license built. – assemble and license designs, in. TajIran – joint venture between Iran Tractor and Homa Company in.
Assembles tractors. – former licensee in. Uzel – Uzel Tractor Plant in. VenIran – joint venture between Iran Tractor and Corporation Venezuela de Guayana in.
Assembles tractors. Zadrugar – of Yugoslavia.
Built the MF 35 under license. born in 2012 of a partnership between the, the Algerian company of distribution of agricultural equipment (PMAT) and the US AGCO Massey Ferguson The factory is producing several Models Massey Ferguson tractors and one tractor.
See also. —area where Massey Ferguson had a plant is now a residential neighbourhood with the company's head office at 915 King Street West still standing (by c.
Rival manufacturers:. References. Pripps, Robert N. The Big Book of Farm Tractors (Vancouver, BC: Raincoast Books, 2001), p. ^, p. 146. ^ Martin, Joseph E.
Canada's History. 97 (5): 47–53. 2012-03-05 at the. Retrieved 2010-05-03. Easterlund, Peter. Easterlund, Peter.
Easterlund, Peter. Easterlund, Peter. Easterlund, Peter. Easterlund, Peter. Easterlund, Peter.
Tanks Encyclopedia. Retrieved 30 March 2016. Military History Encyclopedia of the Web. Retrieved 30 March 2016.
Massey Ferguson 393 Reviews
Victorian Heritage Database Report: Massey Ferguson Complex. The Massey Legacy, by John Farnworth,. FOMCC., pp. 150–1., p. 154., p. 150., p. 158., pp. 160–163. Per MCC Employee.
Sources. Pripps, Robert N. The Big Book of Farm Tractors. Vancouver, BC: Raincoast Books, 2001.
Newman, Peter C. The Establishment Man: A Portrait of Power. McClelland and Stewart, 1982. External links Wikimedia Commons has media related to.